Risk management for forex trading is the process of identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential risks in order to protect your capital and maintain consistent profitability. Without a solid risk management strategy, even the most accurate market analysis can lead to significant losses.
This article explores essential risk management principles and techniques that every Forex trader should implement to protect their capital and optimize trading performance.
Why Is Risk Management Important in Forex Trading?
Forex trading involves significant risks due to the market’s volatility, leverage, and unpredictable factors such as economic news, geopolitical events, and unexpected market movements. Traders who neglect risk management expose themselves to substantial losses, which can quickly erode their trading capital.
Here are key reasons why risk management is essential:
- Capital Preservation: The primary goal of trading is to make a profit, but the first step in achieving this goal is ensuring that you don’t lose your entire capital. Risk management helps prevent significant drawdowns and preserves your funds for future trades.
- Control of Emotions: Managing risk reduces the likelihood of emotional trading. Fear and greed can cloud judgment, leading to impulsive decisions. By having a well-defined risk management strategy, traders are less likely to panic during market fluctuations.
- Sustainable Trading: Traders with a disciplined approach to risk can trade consistently over the long term, avoiding the “boom and bust” cycle where large profits are followed by equally large losses.
Key Principles of Risk Management in Forex Trading
1. Risk-to-Reward Ratio
The risk-to-reward ratio is one of the most fundamental aspects of risk management. It helps traders assess whether a trade is worth the risk taken. A typical rule is to aim for a ratio of 1:2 or higher. This means that for every dollar you risk, you should aim to make at least two dollars in return.
- Example: If you risk $100 on a trade, your potential profit target should be $200. If the market reaches your target, you’ll make twice as much as you risked. Even if you win only 50% of your trades, you’ll still be profitable with a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio.

2. Position Sizing
Position sizing determines how much of your account you are willing to risk on a single trade. It’s a critical part of risk management because it ensures that no single trade can wipe out your account.
- Rule of Thumb: A common recommendation is to risk only 1-2% of your trading capital on any given trade. This means that even if you experience a series of losses, your account won’t be significantly impacted.
- Example: If you have a $10,000 trading account and risk 1% per trade, you would risk $100 per trade. Even after 10 consecutive losses, your capital would still be largely intact.

3. Leverage Control
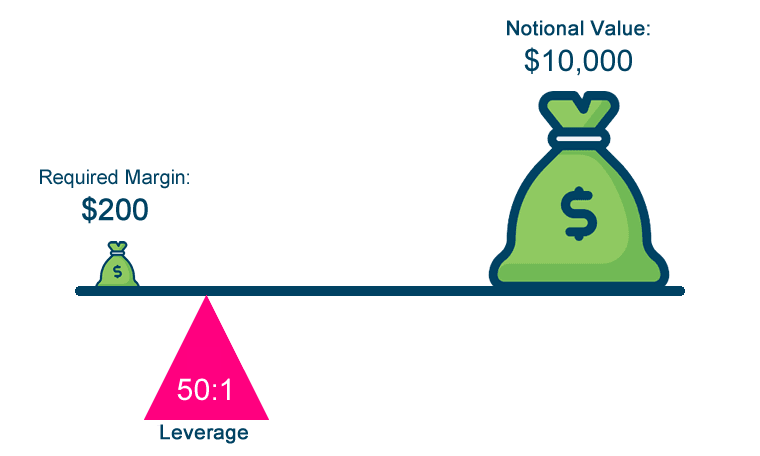
Leverage allows Forex traders to control large positions with a relatively small amount of capital. However, while leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses. Misusing leverage is one of the leading causes of significant losses in Forex trading.
- Strategy: Use leverage cautiously and always consider the potential downside. For beginner traders, it’s advisable to use minimal or no leverage until you gain more experience.
- Example: A 50:1 leverage ratio means that for every $1 in your account, you control $50 worth of currency. While this can increase profit potential, a 2% move against your position could wipe out your entire account.
4. Stop Loss Orders
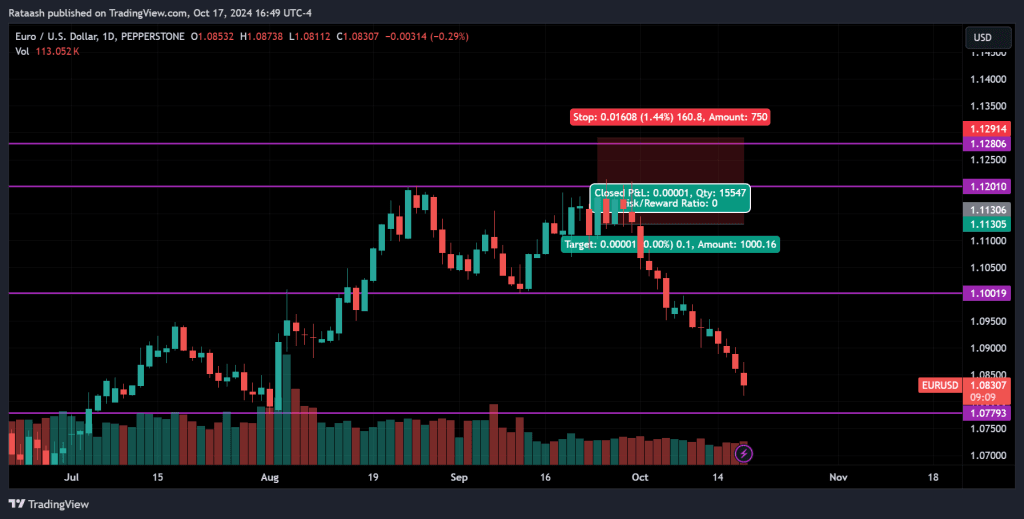
Stop loss orders automatically close a trade when the price reaches a specified level, limiting the amount of loss on a trade. A stop loss is a vital risk management tool as it prevents you from losing more than you’re willing to on a trade.
- Rule: Always use a stop loss on every trade to cap potential losses. Set it at a level that aligns with your overall risk tolerance and strategy.
- Example: If you’re willing to risk $100 on a trade, place your stop loss at a price point where your loss will be limited to $100 if the market moves against you.
5. Take Profit Orders
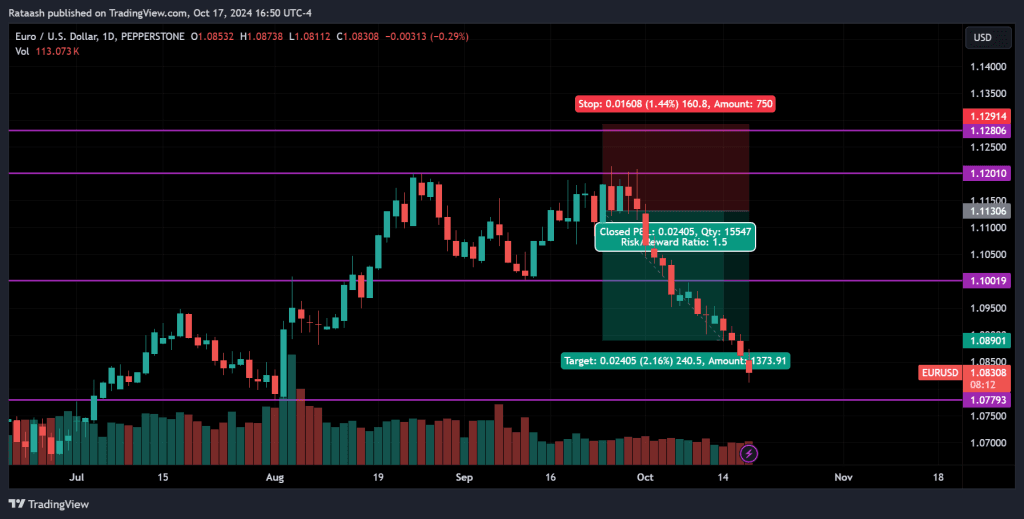
Just as a stop loss protects your downside, a take profit order locks in gains by automatically closing a trade once a specified profit target is reached. This prevents traders from holding onto winning trades too long and giving back profits when the market reverses.
- Strategy: Set your take profit at levels consistent with your risk-to-reward ratio. For example, if you’re risking $100, aim for a take profit that nets you at least $200.
6. Avoiding Overtrading
Overtrading occurs when traders take too many trades in a short period, often driven by the desire to recover losses or capitalize on market trends. Overtrading increases the chances of making impulsive decisions, leading to larger-than-expected losses.
- Strategy: Stick to your trading plan and avoid the temptation to enter multiple trades just because the market is active. Quality over quantity is key in Forex trading.
7. Diversification
Diversification involves spreading your risk across different currency pairs or asset classes. This helps reduce exposure to any single market event or currency.
- Example: Instead of putting all your capital into one trade on the EURUSD pair, consider diversifying across multiple pairs like USDJPY, AUDUSD, and GBPUSD. This way, if one pair experiences significant volatility, your overall risk is spread out.
Advanced Risk Management Techniques
1. Risk Parity
Risk parity is an advanced portfolio management technique that allocates risk across various asset classes to achieve a more balanced portfolio. In Forex trading, this could mean allocating different levels of capital to currency pairs based on their volatility.
- Strategy: If one currency pair is more volatile than another, allocate less capital to it, so that the risk (not the dollar amount) remains equal across all trades.
2. Hedging
Hedging is a strategy used to offset potential losses in one position by taking an opposite position in a related market. While not suitable for all traders, hedging can reduce risk during volatile market conditions.
- Example: If you have a long position in EURUSD, you could hedge by taking a short position in EURGBP, which may move inversely under certain conditions.
3. Trailing Stops
A trailing stop is a dynamic stop loss that moves with the market. It allows traders to lock in profits as the market moves in their favor while still limiting downside risk.
- Example: If you’re long EURUSD at 1.1000 with a trailing stop set at 50 pips, and the price moves to 1.1100, your stop will adjust to 1.1050. If the price reverses and hits your trailing stop, your position will close, securing a 50-pip gain.
Psychological Aspects of Risk Management
Managing risk isn’t just about setting stop losses and managing position sizes—it’s also about mastering the psychological aspects of trading. Traders must develop the discipline to stick to their plan, even when the market moves against them.
- Emotional Control: Avoid making decisions based on fear or greed. Stick to your risk management strategy, and don’t let short-term market movements influence your overall plan.
- Consistency: Successful traders are those who remain consistent in their risk management approach, regardless of market conditions. Consistency helps build confidence and discipline over time.
Conclusion
Risk management is the cornerstone of successful Forex trading. By carefully controlling your exposure to risk, you can protect your capital, reduce emotional stress, and increase the likelihood of long-term profitability. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, implementing the principles outlined in this article will help you navigate the complexities of the Forex market with greater confidence and discipline.
Always remember, in Forex trading, the goal isn’t just to make money—it’s to manage risk effectively so that you can remain in the game for the long haul.


[…] Set firm stop-losses and take-profits and ensure that trades align with the strategy’s risk reward […]