Understanding how to choose a Forex broker can be the deciding factor between a smooth, successful trading journey and one filled with setbacks. Whether you’re an absolute beginner just learning the ropes of currency trading or a seasoned pro refining your strategy, selecting the right broker is a pivotal first step. In this in depth guide, you’ll discover everything you need to know about Forex brokers, how they operate, the different types available, and the essential criteria for evaluation, such as regulation, fees, platforms, and more.
Carefully structured to be both user-friendly and comprehensive, this article goes into detail on each relevant aspect, provides practical examples, and clarifies important concepts. By the end, you’ll be empowered to make informed choices, ensuring that both beginners and experienced traders alike can enjoy a safer and more rewarding trading experience.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Forex Trading

Forex, short for “foreign exchange,” is the global marketplace where currencies are bought and sold. It is arguably the largest and most liquid market in the world, with an average daily trading volume surpassing $6 trillion. This high level of liquidity and round-the-clock nature (trading occurs 24 hours a day, five days a week) make Forex trading appealing to traders of all levels.
Before diving into the detailed process of choosing a broker, it is helpful to understand the basics of how Forex trading works:
- Currency Pairs – In Forex, you trade currencies in pairs (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/JPY). The first currency is the base currency, and the second is the quote currency.
- Bid and Ask Prices – Every currency pair quote has two prices—a bid (sell price) and an ask (buy price). The difference between these two prices is called the spread.
- Leverage – Most Forex brokers offer leverage, which allows you to control a larger position in the market with a smaller amount of capital. While leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses.
- Market Sessions – Although the Forex market is decentralized and trades globally, it is commonly broken down into major trading sessions: London, New York, Sydney, and Tokyo.
Understanding these fundamental concepts lays a groundwork for evaluating which broker and trading style might suit you best.
2. What Is a Forex Broker?
A Forex broker is a financial services firm that provides traders access to a platform for buying and selling foreign currencies. These brokers act as intermediaries: when you place a trade, your order is executed either by the broker directly (in the case of a Market Maker) or routed to liquidity providers (in the case of ECN/STP brokers).
Functions of a Forex Broker
- Order Execution – Brokers facilitate the buying and selling of currencies. Depending on the broker type, they may act as a counterparty to your trades or pass your trades to external liquidity providers.
- Provision of Trading Platforms – Most brokers offer trading platforms such as MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), or proprietary platforms. These platforms come equipped with charts, technical indicators, and other tools.
- Leverage and Margin – Brokers provide leverage to traders, enabling them to open positions that exceed their actual account balance. They also set margin requirements, which determine how much capital you must maintain.
- Customer Support and Resources – Good brokers offer educational materials, market analysis, and customer support to assist traders at various stages of their trading journey.
- Risk Management – Some brokers provide features like negative balance protection, guaranteed stop losses, and other risk management tools to help you protect your capital.
Because the foreign exchange market is largely unregulated on a global scale (it is decentralized), choosing a broker that is reputable, well-regulated, and aligned with your trading goals is absolutely crucial.
3. Why Choosing the Right Forex Broker Matters
Selecting a broker is not just about picking a random company that allows you to trade currency pairs. Your choice of broker can significantly affect:
- Your Profitability – Different brokers offer different spreads, commissions, and execution speeds. High spreads or frequent platform outages can severely impact your ability to capitalize on profitable trades.
- Your Safety of Funds – A broker’s regulatory status and financial stability are vital for ensuring your funds remain secure. In cases of broker insolvency or malpractice, regulation and compensation schemes can offer crucial protection.
- Your Overall Trading Experience – The right broker will provide a stable, user-friendly platform, reliable customer service, and educational resources that can streamline your path to success.
- Your Ability to Develop and Implement Strategie – Some brokers limit the types of strategies you can use, such as scalping or hedging. In contrast, others might offer advanced tools to facilitate algorithmic trading or social trading.
Whether you are a beginner looking for a simple entry point or a professional seeking advanced features, it is imperative to evaluate brokers based on your personal trading needs, risk tolerance, and objectives.
4. Types of Forex Brokers
Different brokers operate under different business models, each with pros and cons. Understanding these models allows you to choose the one that best fits your trading style, risk tolerance, and preferences.
Market Maker Brokers (Dealing Desk)
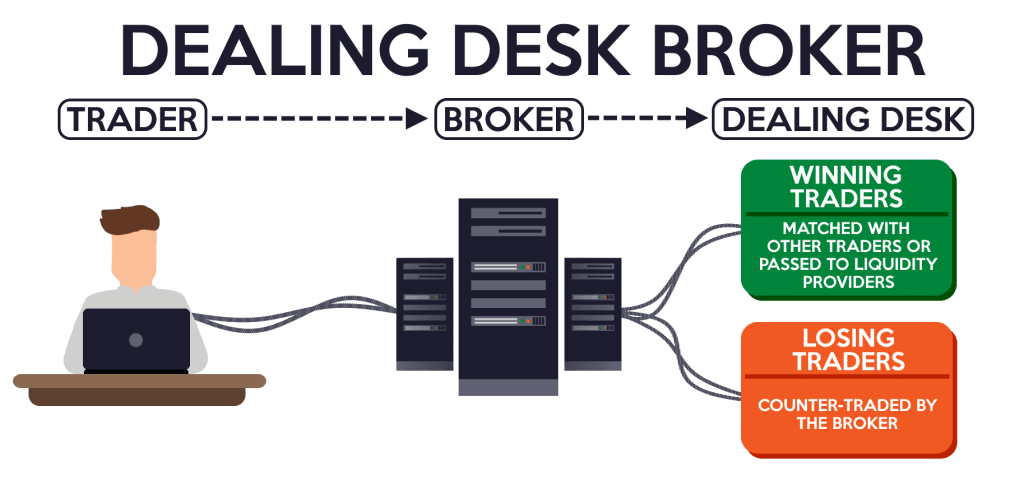
A Market Maker (sometimes referred to as a Dealing Desk broker) takes the opposite side of your trade. Essentially, the broker “creates the market” for its clients, quoting both the bid and ask prices internally.
How They Work
- When you place a buy or sell order, the broker may match your trade internally against other client orders or take the trade itself.
- Market Makers earn primarily from the spread and can also benefit if the client loses, since the broker might be the counterparty.
Pros
- Fixed Spreads: Often, Market Makers can offer fixed spreads, which is beneficial in volatile market conditions.
- Lower Capital Requirements: Market Makers typically cater to retail traders who are just starting and may not require large initial deposits.
Cons
- Potential Conflict of Interest: Since the broker may profit if you lose, there is a perceived conflict of interest.
- Requotes and Slippage: Especially during times of high volatility, you may experience requotes or slippage more frequently.
Market Maker brokers can be suitable for beginner traders who appreciate simplicity, fixed spreads, and smaller initial capital requirements. However, traders who want direct market access or worry about conflicts of interest may look elsewhere.
ECN (Electronic Communication Network) Brokers
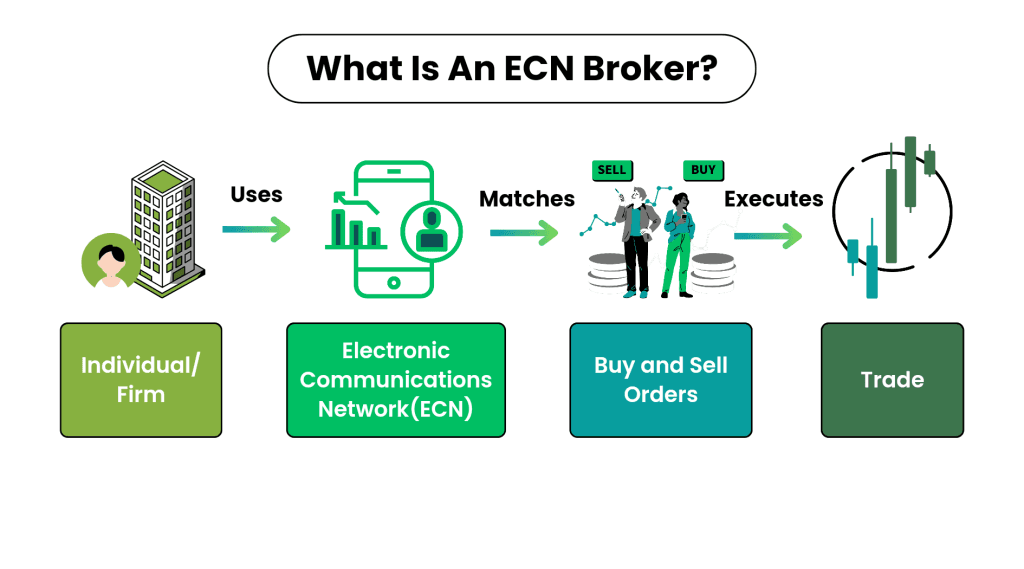
An ECN broker provides a platform where traders can directly interact with liquidity providers—such as banks, financial institutions, and other traders—through an electronic communication network. The broker’s role is to match buy and sell orders in real-time.
How They Work
- ECN brokers typically charge commissions on top of raw spreads that come from the interbank market.
- They do not take the opposite side of your trade. Instead, they pass your order directly into the network where it competes with other market participants.
Pros
- Tight Spreads: Often very tight spreads, especially in highly liquid currency pairs.
- No Dealing Desk Intervention: Reduced conflict of interest; your broker is not taking the other side of your trades.
- Transparency: ECN quotes are more transparent, with prices aggregated from multiple liquidity providers.
Cons
- Variable Spreads: While spreads can be extremely low, they are not fixed and can widen during low-liquidity periods or major news events.
- Higher Minimum Deposits: Some ECN brokers require larger initial deposits.
- Commission Costs: Commissions can add up, particularly for high-volume traders.
ECN brokers are popular among experienced traders, scalpers, and algorithmic traders who appreciate direct market access, transparency, and tight spreads. However, beginners may find ECN accounts slightly more complex, especially if they are not prepared for variable spreads and commission structures.
STP (Straight Through Processing) Brokers
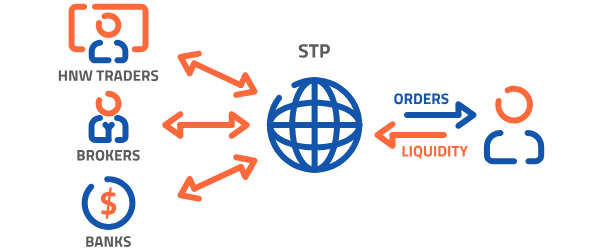
STP (Straight Through Processing) brokers act as intermediaries that send your orders directly to their liquidity providers—banks, hedge funds, or other large brokerages—without a dealing desk in-house.
How They Work
- STP brokers pool liquidity from multiple providers to offer competitive spreads to their clients.
- Similar to ECN brokers, they earn either through a markup on the spread or a small commission per trade, though STP markups are more common.
Pros
- Fewer Conflicts of Interest: Orders are routed externally rather than matched internally.
- Potentially Better Execution: STP brokers can provide quick execution times, making them suitable for day traders and scalpers.
- Competitive Spreads: Because STP brokers source quotes from multiple liquidity providers, spreads can be quite competitive.
Cons
- Variable Spreads: Like ECN brokers, STP spreads can widen during low-liquidity periods or volatile market conditions.
- Less Transparent Pricing Compared to ECN: Although STP brokers receive quotes from liquidity providers, they sometimes add hidden markups.
For traders who seek a balance between the ease of a Market Maker and the direct market access of an ECN, STP brokers can be a compelling option. They often cater to a broad range of traders, from beginners to professionals.
DMA (Direct Market Access) Brokers
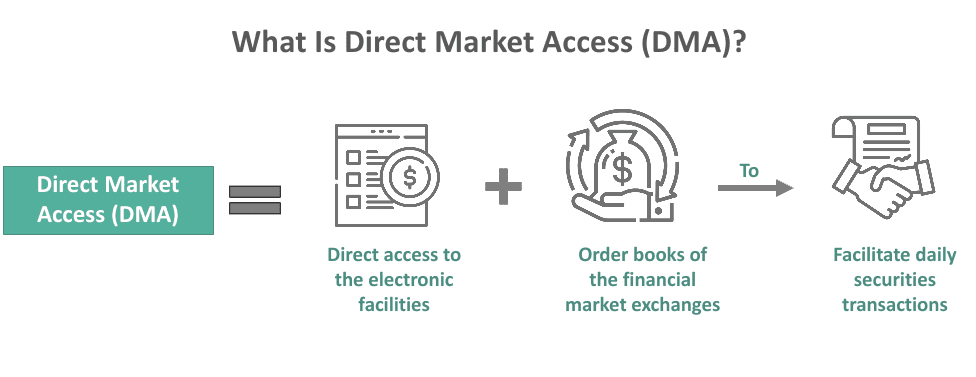
Direct Market Access (DMA) brokers enable traders to place orders directly into the order book of an exchange or a liquidity provider. While often associated with equity and futures markets, DMA functionality also applies to Forex trading under certain brokerage structures.
How They Work
- DMA brokers offer a transparent view of market depth (Level 2 or Level 3 data), showing real-time bids and offers from various participants.
- Trades bypass any internal dealing desk and go straight to the liquidity venue.
Pros
- Full Transparency: Traders can see the order book depth and decide at which price levels they want to execute.
- Potentially Better Pricing: By interacting directly with the market, traders may achieve better pricing and lower slippage.
- Ideal for Professional Traders: DMA is favored by advanced traders who need granular control.
Cons
- Higher Complexity: Beginners may find DMA platforms complex and overwhelming.
- Possible Higher Capital Requirements: DMA accounts can require significant minimum deposits.
- Platform Fees: Some DMA brokers charge additional platform or market data fees.
DMA is generally best suited for professional traders, institutional clients, or highly active retail traders who require the utmost transparency and control over their executions.
Hybrid Brokers
Hybrid brokers combine multiple models (like Market Maker and STP, or STP and ECN) under one roof. They might route certain orders through their dealing desk if the order size is small, while larger or more sophisticated orders may go straight to their liquidity providers.
How They Work
- A hybrid broker can offer different account types—some structured as Market Maker accounts with fixed spreads, others as ECN/STP accounts with raw spreads plus commissions.
- They manage order flow based on internal policies, sometimes analyzing the profitability of client orders before deciding how to execute them.
Pros
- Flexibility: Traders can choose from multiple account types and fee structures depending on their needs.
- Scalability: Hybrid brokers often allow traders to upgrade accounts as they gain experience or increase trading volume.
Cons
- Lack of Transparency: It might be unclear which trades go to the market and which stay in-house.
- Potential Conflicts of Interest: Some trades may be handled via a dealing desk, which can be concerning for transparency-focused traders.
Hybrid brokers aim to cater to a wide array of traders, from newbies requiring fixed spreads and simple setups to experts seeking raw spreads and direct execution.
5. Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Forex Broker
Selecting the right broker involves more than just picking a known brand. You should conduct thorough due diligence on various elements, from regulation to customer service. Below are the key factors you should prioritize when evaluating any Forex broker.
5.1 Regulation and Licensing

Regulation is arguably the most crucial factor when choosing a Forex broker. Different countries have different regulatory bodies, each with varying degrees of oversight and protection for traders.
Major Regulatory Authorities
- U.S. – The National Futures Association (NFA) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC)
- U.K. – The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA)
- Australia – The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC)
- Cyprus – The Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC)
- Japan – The Financial Services Agency (FSA)
Regulated brokers must adhere to strict guidelines, including maintaining sufficient capital reserves, segregating client funds, and reporting regularly. This compliance helps ensure the broker can honor withdrawal requests and reduces the risk of fraud.
Red Flags of Poor or Non-Existent Regulation
- Operating from “Offshore” Jurisdictions – Some brokers choose loosely regulated jurisdictions to evade strict financial scrutiny.
- Lack of Licensing Information – Brokers that do not display their license numbers or regulatory bodies on their websites might be hiding something.
- No Independent Audit Reports – Reputable brokers often undergo external audits to validate their financial stability.
Tip: Always verify a broker’s license on the official website of the regulatory body. Do not rely solely on a broker’s claims or marketing materials.
5.2 Trading Platforms and Tools

The trading platform is your gateway to the Forex market. A well-designed, stable platform can significantly enhance your trading experience, while a glitch-prone platform can cause lost opportunities or unexpected losses.
Commonly Used Platforms
- MetaTrader 4 (MT4) – Known for its user-friendly interface, charting tools, Expert Advisors (EAs), and wide broker support.
- MetaTrader 5 (MT5) – Similar to MT4 but with more asset classes (stocks, futures, etc.), advanced charting, and order management features.
- cTrader – Popular among ECN/STP traders for its depth of market (DOM) features and clean interface.
- Proprietary Platforms – Some brokers have their own proprietary platforms, which may offer unique features or advanced functionalities.
Key Platform Features to Evaluate
- Stability and Reliability – How often does the platform crash or freeze? Stability is paramount, particularly in volatile markets.
- Charting and Technical Analysis Tools – Are there enough technical indicators and drawing tools to support your trading strategy?
- Order Types – Does the platform allow different order types (market, limit, stop-limit, etc.) and advanced functionalities like trailing stops?
- Algorithmic Trading – If you’re interested in automated trading, check if the platform supports Expert Advisors (EAs) or similar automation features.
- Mobile Compatibility – For traders on the go, mobile apps should be user-friendly and stable.
A broker that offers multiple platform options might be more flexible and cater to a broader range of traders.
5.3 Spreads, Commissions, and Other Fees
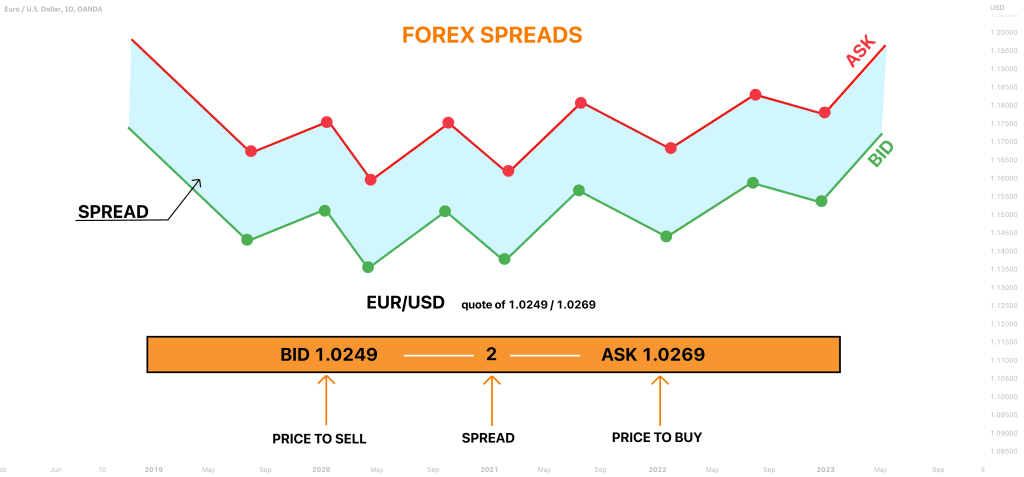
Fees eat into your profits, so understanding the cost structure is crucial. Forex brokers typically earn money through spreads, commissions, or a combination of both.
Types of Fee Structures
- Spread-Only Model – Many Market Makers or STP brokers quote a spread (the difference between the bid and ask price). This spread could be fixed or variable.
- Raw Spread + Commission Model – ECN brokers often provide very tight spreads but charge a commission per lot traded.
- Hybrid Model – Some brokers charge both a small markup on the spread plus a commission.
Other Possible Fees
- Overnight Swap Fees (Rollover Fees) – If you hold positions overnight, you might incur or earn interest based on the currency pair’s interest rate differential.
- Deposit and Withdrawal Fees – Some brokers charge for deposits or withdrawals via certain payment methods.
- Inactivity Fees – If you do not trade for a certain period, the broker may charge an inactivity fee.
- Account Maintenance Fees – Less common in Forex but still possible with some brokers.
Tip: Calculate your potential monthly or yearly costs by factoring in your expected trade volume, spreads, commissions, and swap rates. Even small differences in spreads can amount to significant costs over time if you trade frequently.
5.4 Leverage and Margin
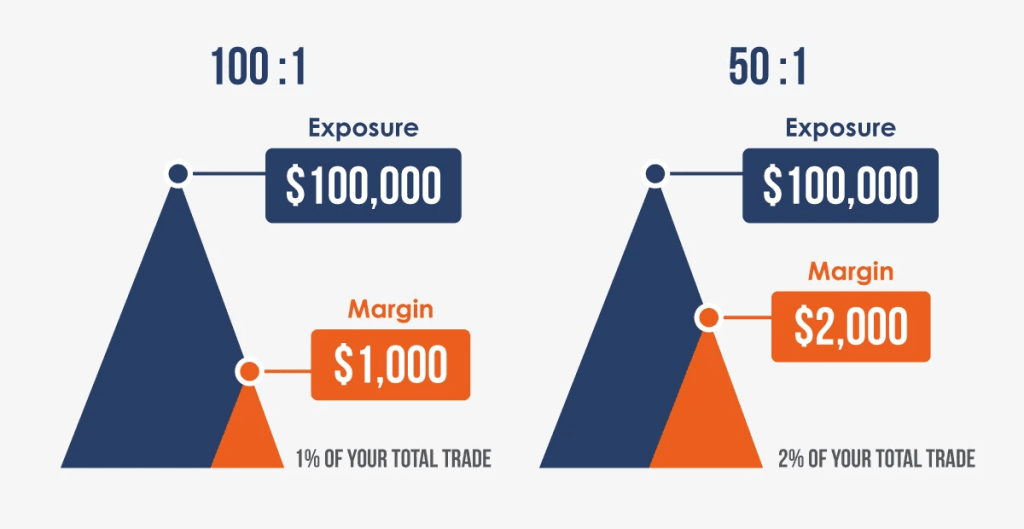
Leverage is a double-edged sword. While high leverage allows you to magnify profits on relatively small moves in currency prices, it also increases your downside risk. Brokers can offer varying leverage ratios depending on their regulatory constraints and internal policies.
- High Leverage (e.g., 1:500, 1:1000) – Attractive for high-risk, high-reward strategies. However, it also puts you at risk of losing money quickly if the market moves against you.
- Moderate Leverage (e.g., 1:50, 1:100) – Commonly available in strictly regulated regions (like the U.S.). Provides a balance between potential returns and risk.
Margin Calls and Stop-Out Levels
- Margin Call – Occurs when your account equity drops below the broker’s required margin level. The broker may require you to deposit more funds.
- Stop-Out Level – If your account continues to lose value, positions may be automatically closed to prevent the account from going negative.
Tip: Always manage leverage wisely. A responsible approach is to use lower leverage until you gain experience and have a solid risk management strategy in place.
5.5 Deposit and Withdrawal Options

Ease of depositing and withdrawing funds can significantly impact your trading experience. Look for brokers that offer a variety of payment methods and process requests efficiently.
Common Payment Methods
- Bank Wire Transfer – Secure but can be slow (up to several business days).
- Credit/Debit Cards – Faster processing, usually instant deposits; fees may apply.
- E-Wallets (PayPal, Skrill, Neteller) – Often instant, but some brokers may add fees.
- Cryptocurrencies – An emerging option for instant deposits/withdrawals, though not universally supported.
Processing Times
- Deposits – Typically instant with credit/debit cards or e-wallets, while bank wires might take a few days.
- Withdrawals – Can take anywhere from a few hours (for e-wallets) to several business days (for bank wires).
Tip: Check the broker’s withdrawal rules. Some brokers require you to withdraw via the same method you used to deposit, while others restrict certain methods based on regional regulations.
5.6 Customer Service and Support

Reliable customer service can be a lifesaver, especially when dealing with urgent issues like platform malfunctions, withdrawal delays, or account verification. The quality of support is one differentiator between top-tier and mediocre brokers.
Key Points to Assess
- Availability – Is customer service available 24/5 or 24/7?
- Channels: Live chat, email, phone, messaging apps like WhatsApp or Telegram.
- Language Support – Does the broker offer support in your preferred language?
- Technical Expertise – Are support agents knowledgeable enough to solve your trading-related issues promptly?
Reading online reviews and testing their customer support with a few queries (via live chat or email) before opening an account can give valuable insights into the broker’s responsiveness.
5.7 Educational Resources and Research Tools
Whether you are a novice or an experienced trader, quality educational materials and market research can enhance your trading skills and decision-making.
Types of Educational and Research Offerings
- Video Tutorials and Webinars – Ideal for visual learners who want to learn about trading strategies, platform usage, or market analysis.
- Ebooks and Articles – Written content covering various topics from risk management to advanced trading strategies.
- Interactive Courses – Some brokers partner with professional traders or educators to offer structured courses.
- Market Analysis and Economic Calendars – Fundamental analysis tools that highlight upcoming economic events, market news, and trading signals.
Brokers that invest in educational resources often demonstrate a commitment to client success. This can be especially valuable for beginners seeking a supportive learning environment.
5.8 Bonus Features (Copy Trading, Social Trading, etc.)
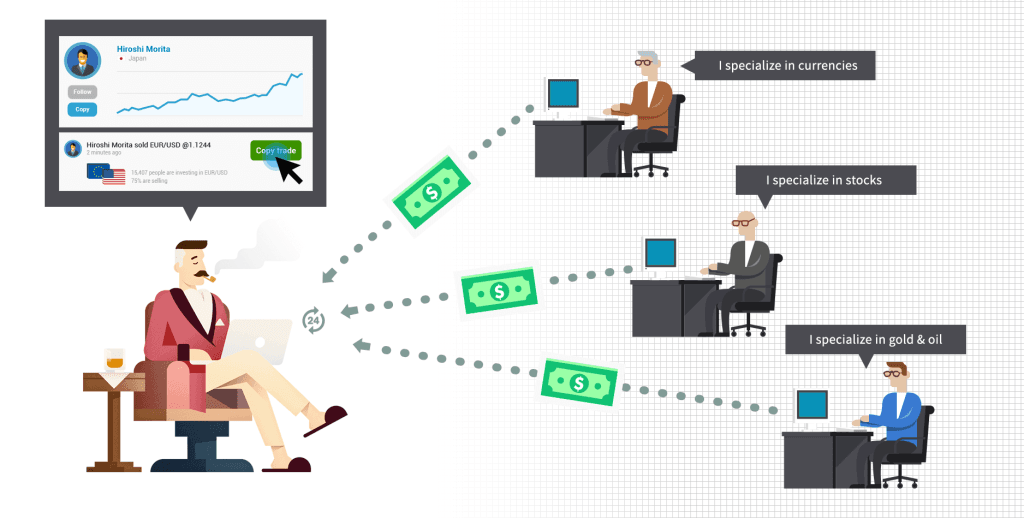
In today’s competitive market, many brokers provide value-added features to stand out. These can include:
- Copy Trading – Allows you to automatically replicate trades of successful traders.
- Social Trading – Enables interaction with other traders, sharing strategies, and market insights in a social media-like platform.
- VPS Hosting – For algorithmic traders running Expert Advisors 24/7, a Virtual Private Server (VPS) can ensure uninterrupted connectivity.
- Trading Signals and Automated Systems – Some brokers offer proprietary signals or partner with third-party signal providers.
If these features are important to you, make sure to check a broker’s offerings and whether they align with your trading style.
6. Steps to Evaluate a Forex Broker
Selecting a suitable broker is a multi-step process that requires a systematic approach:
- Identify Your Trading Needs – Determine your objectives, preferred trading style, risk tolerance, and desired features (e.g., scalping, copy trading).
- Shortlist Reputable Brokers – Focus on brokers with robust regulation, good track records, and positive user reviews.
- Examine Fee Structures – Compare spreads, commissions, swaps, and other charges.
- Test Trading Platforms – Open demo accounts (if available) to evaluate platform stability, charting tools, and ease of use.
- Assess Customer Support – Reach out to the broker’s support team to gauge response times and professionalism.
- Review Terms and Conditions – Carefully read the broker’s policies on deposits, withdrawals, inactivity, bonuses, and more.
- Start Small – Open a live account with a minimal deposit to test execution, slippage, and overall reliability. If satisfied, consider scaling up.
Performing each step thoroughly increases your chances of finding a reliable broker that meets your trading needs.
7. How to Test a Forex Broker
Once you have narrowed down your broker choices, conducting a thorough test can provide valuable insights:
- Open a Demo Account – This allows you to test the platform’s features without risking real money. Pay attention to execution speeds, charting tools, and ease of navigation.
- Check Execution on a Small Live Account – Demo environments might differ from real-market conditions. Testing with a small live account reveals true spreads, slippage, and trade execution times.
- Monitor Spreads During News Events – Spreads can widen during high-volatility periods. Observe how the broker handles these conditions.
- Observe Platform Stability – Check for crashes, freezes, or disconnections, especially during busy market hours.
- Initiate Deposits and Withdrawals – Ensure the broker processes transactions quickly and without hidden fees.
- Contact Customer Support – Try various methods (live chat, phone, email) to test responsiveness and problem-solving skills.
By performing these checks, you can confirm whether the broker meets your expectations in real-world trading environments.
8. Common Mistakes When Choosing a Forex Broker
- Ignoring Regulation – Trading with an unregulated broker to chase high leverage or sign-up bonuses can be risky.
- Focusing Solely on Spreads – While spreads are important, factors like execution quality, customer service, and platform stability are equally crucial.
- Skipping the Fine Print – Overlooking hidden fees, margin requirements, or withdrawal policies can lead to unpleasant surprises.
- Not Considering Your Trading Style – A broker that prohibits scalping is unsuitable for scalpers, for instance.
- Overlooking Customer Support – Inadequate support can be frustrating when technical or account issues arise.
- Failing to Test with a Live Account – Conditions in a demo account can differ, so always test with a small live account before committing significant funds.
Avoid these pitfalls by doing your due diligence and remaining mindful of your specific trading needs and preferences.
9. Examples of How Different Broker Types Suit Different Traders
Below are some scenarios illustrating how certain broker models or account types fit various trading styles:
Beginner Trader, Small Capital
- Broker Type: Market Maker
- Reasoning: Fixed spreads, lower capital requirements, and often more educational resources.
- Example: John is new to Forex and wants a straightforward platform with minimal surprises. A Market Maker broker that offers a cent or micro account might be ideal.
Scalper or High-Frequency Trader
- Broker Type: ECN or STP
- Reasoning: Tight spreads and fast execution are crucial for high-frequency trading.
- Example: Sarah trades the EUR/USD pair with short time frames, aiming for small profits per trade. She benefits from an ECN broker offering raw spreads and rapid order execution.
Algorithmic Trader
- Broker Type: ECN or DMA
- Reasoning: Direct market access, low latency, and robust platform compatibility (e.g., MetaTrader 5, cTrader) are necessary for automated strategies.
- Example: Alex runs Expert Advisors around the clock. An ECN broker with VPS support and stable servers is essential for seamless trade execution.
Swing Trader Focused on Major Currency Pairs
- Broker Type: STP or Hybrid
- Reasoning: Competitive variable spreads, moderate commission or markup, and flexible leverage.
- Example: Emily holds positions for several days or weeks, so she doesn’t require ultra-tight spreads but values a balance of cost-effectiveness and platform reliability.
Professional Trader Looking for Market Depth
- Broker Type: DMA
- Reasoning: Access to Level 2 or Level 3 market data, complete transparency, and direct market order placement.
- Example: Victor trades large volumes in multiple asset classes. A DMA solution offering advanced market data and deep liquidity is optimal.
These examples highlight the importance of matching your trading goals, strategy, and experience level with the appropriate broker model.
10. Final Thoughts
Choosing the right Forex broker is a crucial decision that affects almost every aspect of your trading journey from order execution and cost to the security of your funds and overall trading experience. By carefully analyzing factors such as regulation, fee structures, platform capabilities, and customer support, you can narrow down your options to a shortlist of brokers that genuinely meet your needs.
Check Out our Forex Broker List
Remember, the Forex market presents significant opportunities but also substantial risks. Being meticulous in your choice of broker is part of responsible trading, ensuring you have a trustworthy partner and a stable environment in which to execute trades. Whether you are a beginner setting up your first account or a professional trader fine-tuning your approach, the broker you pick will play a decisive role in your success.
11. FAQs
Below are some frequently asked questions that can further clarify how to choose the most suitable Forex broker.
How much money do I need to start trading Forex?
The amount required can vary widely. Some brokers offer micro accounts or cent accounts that allow you to start with as little as $10 or $100. However, to have adequate risk management and avoid over-leveraging, many traders recommend starting with at least $500 to $1,000.
Is it safe to trade with offshore or unregulated brokers?
Trading with offshore or unregulated brokers increases your risk. In these scenarios, you have minimal legal recourse if the broker engages in fraudulent activities or becomes insolvent. It is generally advisable to choose brokers regulated by well-known financial authorities.
Which trading platform is best for beginners?
MetaTrader 4 (MT4) is often the go-to choice for beginners due to its intuitive interface and extensive educational resources available online. Many brokers also provide user-friendly proprietary platforms with simplified features aimed at new traders.
How important is trading psychology when selecting a broker?
While trading psychology is crucial for success, it’s only indirectly related to your broker choice. However, features that promote better risk management—like negative balance protection—can alleviate some psychological stress. Good customer support and educational resources can also help you develop a disciplined approach.
Do all brokers allow scalping or hedging?
Not all brokers permit scalping (opening and closing positions within seconds) or hedging (opening opposite positions in the same instrument). Always review the broker’s terms and conditions to ensure your preferred strategies are allowed.
Why do spreads widen during market volatility?
Spreads widen during high volatility because liquidity providers may widen their own quotes to compensate for increased risk. ECN/STP brokers pass on these wider spreads directly to traders, while Market Makers might opt for fixed spreads but can introduce requotes instead.
Can I open multiple accounts with the same broker?
Yes. Many traders open multiple accounts for different strategies (e.g., one for scalping, another for swing trading). Just make sure to check the broker’s policy on multiple accounts and whether additional fees apply.
How do I verify if a broker is truly regulated?
Visit the official website of the regulatory authority (e.g., FCA in the UK) and enter the broker’s license number. You can typically find this number on the broker’s website or marketing materials. If the broker is not listed in the regulator’s database, consider it a red flag.
Is a bonus offer a good reason to choose a broker?
Not necessarily. While bonuses can be attractive, you should carefully read the terms and conditions. Some bonuses come with restrictive requirements (e.g., high trading volume before you can withdraw funds). It’s better to choose a broker based on factors like regulation, spreads, and platform reliability rather than relying on promotions.
Do all brokers offer negative balance protection?
No. Negative balance protection ensures that you cannot lose more than your deposit. Some regulators (e.g., in the EU) mandate it, but it’s not universal. Always check the broker’s policy if this protection is important to you.
Key Takeaways for Successful Broker Selection
- Regulation and Security: Always prioritize brokers regulated by reputable authorities.
- Transparent Fee Structures: Understand all possible costs—spreads, commissions, swaps, withdrawal fees—to avoid hidden charges.
- Platform and Tools: Choose a stable platform that supports your trading style, whether it’s scalping, algorithmic trading, or long-term investing.
- Customer Support: A knowledgeable and responsive support team can be invaluable when issues arise.
- Align with Your Needs: The best broker for you is the one that aligns with your financial goals, trading style, and risk tolerance.
By following the guidelines in this article, performing due diligence, and testing brokers with small live accounts, you will be well-equipped to find a Forex broker that suits your needs whether you’re just starting out or looking to elevate your trading to the next level.
