In the world of Forex trading, many strategies cater to different trader profiles, risk appetites, and market conditions. One such method, popular among beginners and experienced traders alike, is scalping a fast-paced approach that seeks to capitalize on small price movements over very short timeframes. When implemented correctly, especially in a volatile market, scalping can deliver quick profits in a matter of minutes.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the Volatile Market Scalping Strategy, exploring everything from the basics of volatility to step-by-step trading tactics, risk management, and real-world examples. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of how to scalp in the Forex market and how to optimize your results, even if you are just starting out.
Table of Contents
Understanding Volatility and Scalping
What Is Volatility in Forex?
Volatility refers to how much the price of a currency pair (or any financial instrument) fluctuates over a given period. High volatility implies frequent and sometimes dramatic price moves. Low volatility suggests that prices move more slowly or remain confined in a narrow range.
- Factors Affecting Volatility:
- Economic data releases (e.g., Non-Farm Payrolls, central bank announcements)
- Political events (e.g., elections, referendums)
- Market sentiment (e.g., risk-on vs. risk-off environment)
- Why Volatility Matters for Traders:
- Opportunities for Profit – Big price swings create multiple entry and exit points.
- Risk Considerations – Larger movements also mean greater risk if trades go against you.
What Is Scalping?
Scalping is a short-term trading approach where traders open and close positions within minutes sometimes seconds to capture small yet frequent profits. Scalpers typically hold trades for a few minutes at most, aiming to make the most out of short-lived market movements.
- Typical Scalping Characteristics:
- Short time frames – 1-minute, 5-minute, or sometimes tick charts.
- Small profit targets – 5–10 pips (or even less) per trade.
- High trade frequency – Multiple trades can be taken throughout a trading session.
Why Scalping Works Best in Volatile Markets
The success of a scalping strategy often hinges on the speed and magnitude of price movements. In a volatile market, prices can quickly move from one level to another, providing multiple opportunities to jump in and out with small gains. If the market is slow and range-bound, scalpers may struggle to find trades that yield enough profit to offset transaction costs (spread, commissions, etc.).
- Faster Profit Potential – High volatility can allow trades to hit your profit target quicker.
- Multiple Entries/Exits – Price whipsaws and frequent fluctuations create new opportunities.
- Risk Control – If managed carefully with tight stops, scalpers can exit a losing position rapidly.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Scalping in Volatile Markets
Before diving into the nitty-gritty, it’s crucial to understand the pros and cons of scalping, especially in a market characterized by high volatility.
Advantages
- Quick Profits – Because scalping targets small price movements, you can realize profits quickly, sometimes within seconds.
- Lower Market Exposure – Since scalping involves brief trade durations, you are less exposed to market risks like unexpected news or sudden price crashes over long periods.
- Many Opportunities – Volatile markets move more rapidly, offering multiple scalping opportunities throughout a single session.
Disadvantages
- High Transaction Costs – Scalpers execute many trades, so spreads and commissions can eat into profits.
- Requires Intense Focus – You must constantly monitor the charts to catch fast-moving setups. Scalping can be mentally exhausting.
- Tight Risk Management Needed – While you can profit quickly, you can also lose quickly. If stops are not placed effectively, a single wrong trade in a volatile market can wipe out multiple winning trades.
Key Currency Pairs and Trading Sessions for High Volatility

Major Currency Pairs
Major pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF, AUD/USD, and USD/CAD are some of the most actively traded currencies in the Forex market. High liquidity translates to tighter spreads, which is advantageous for scalpers looking to keep transaction costs low.
- EUR/USD: Typically exhibits moderate to high volatility during the London and New York sessions.
- GBP/USD: Known for more pronounced moves, particularly during the London session when UK economic news is released.
- USD/JPY: Can be highly active during the Asian and overlapping New York sessions.
Cross Pairs
Cross pairs, such as EUR/GBP, GBP/JPY, or EUR/JPY, can also showcase significant volatility. While liquidity may be slightly lower compared to major pairs, some cross pairs are known for robust intraday movements, providing excellent scalping opportunities.
- GBP/JPY: Often termed the “Dragon” because of its reputation for volatile price swings.
- EUR/GBP: Typically more moderate in volatility, but can spike around Eurozone or UK economic data.
Exotic Pairs
Exotic pairs involve a major currency alongside the currency of a developing economy (e.g., USD/TRY, USD/MXN). These pairs can be extremely volatile, but they come with wider spreads and lower liquidity, making them riskier and less ideal for scalping, especially for beginners.
- Pros: Potentially large intraday price swings.
- Cons: High spreads and possible execution issues, which can diminish scalping profits.
Optimal Trading Sessions for Volatility
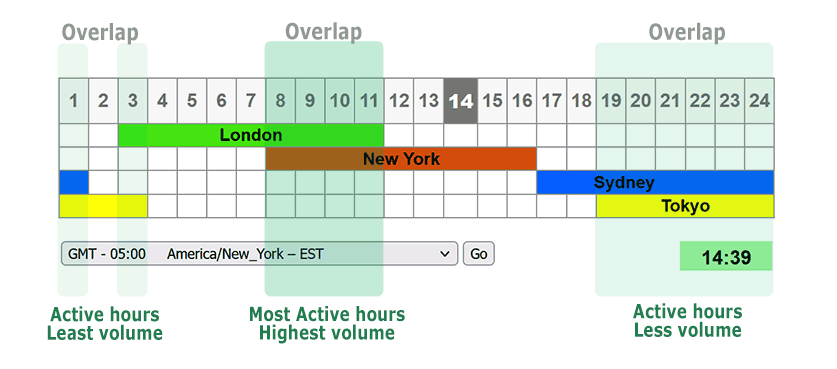
Forex operates 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, but not all sessions are created equal regarding volatility:
- London Session (08:00–16:00 GMT) – Typically features high liquidity and volatility, especially for EUR, GBP pairs.
- New York Session (13:00–21:00 GMT) – Overlaps with London, creating the most liquid time of the day for major pairs.
- Asian Session (00:00–08:00 GMT) – Generally calmer, but pairs like AUD/USD, NZD/USD, and USD/JPY can see decent activity, particularly when major data releases or Bank of Japan announcements occur.
For scalping in a volatile market, the overlap between London and New York (approximately 13:00–16:00 GMT) is often the most active and can present numerous trading opportunities.
Essential Tools and Indicators for Scalping
1. Candlestick Charts
Candlestick charts are the foundational tool for most technical traders, including scalpers. They provide visual cues about price action, such as open, close, high, and low prices within your chosen timeframe.
- Candlestick Patterns: Certain formations like doji, engulfing, and pin bars can indicate potential reversals or continuations, which are valuable signals for scalpers.
2. Moving Averages
Moving Averages (MAs) are commonly used to identify the trend and smooth out short-term price fluctuations.
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Gives equal weight to all price data in a chosen period.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Places more weight on recent data, making it more responsive to current price changes (often preferred by scalpers).
A popular setup is using two EMAs (e.g., a 50-period and a 100-period EMA on a 1-minute or 5-minute chart) to determine overall short-term market direction.
3. Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands consist of a moving average with two standard deviation lines, forming an upper and lower band around the price. The width of the bands expands and contracts based on volatility.
- Scalping Usage:
- Look for price to bounce off the upper or lower band.
- When the bands widen, expect increased volatility.
4. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
RSI measures the speed and magnitude of price changes, oscillating between 0 and 100. Typically, readings above 70 suggest overbought conditions, while readings below 30 suggest oversold conditions.
- Scalping Usage:
- A quick indicator to gauge potential reversals in a volatile market.
- Combine with price action to confirm entries.
5. Stochastic Oscillator
Similar to RSI, the Stochastic Oscillator helps identify overbought and oversold zones but uses a different calculation method based on closing price relative to a range.
- Scalping Usage:
- Can provide quick entry signals in tandem with candlestick patterns.
- Values above 80 = overbought, below 20 = oversold.
6. Support and Resistance Levels
These are price levels where the market has historically reacted. Support is a level below the current price where buying interest may prevent further declines. Resistance is a level above the current price where selling interest may cap further increases.
- Scalping Usage:
- Identify potential bounce or breakout points.
- Look for confluence with indicators or candlestick patterns to refine entries.
7. Price Action Analysis
Beyond mechanical indicators, understanding price action and the raw movement of price on the chart offers invaluable insights. Observing how candles form in real-time can help you gauge market sentiment. For instance:
- Bullish Engulfing Candle: Suggests a possible upward continuation when it appears near support.
- Bearish Engulfing Candle: Indicates potential downward movement near resistance.
Step-by-Step Volatile Market Scalping Strategy
Step 1: Identify the Trend or Market Direction
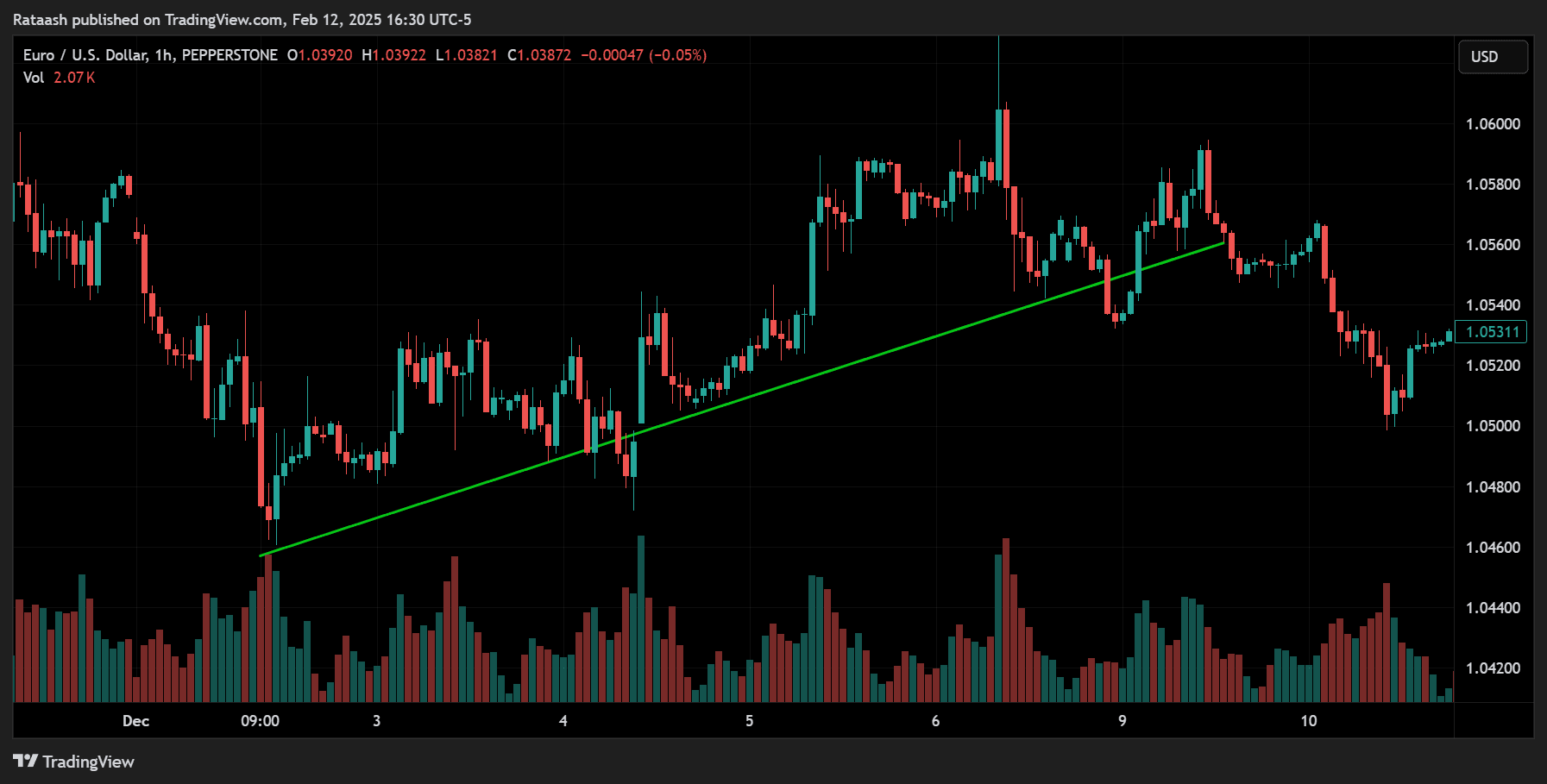
Before placing a scalp trade, you need to assess the overall market direction. Although scalpers use short time frames, analyzing the broader trend (using the 15-minute or 30-minute charts) helps align trades with the market’s momentum.
- Tools: Moving Averages or simply drawing trendlines on higher time frames (15-minute or 30-minute).
- Goal: Trade in the direction of the trend whenever possible. If the larger trend is bullish, look for bullish scalping setups on the smaller timeframe (1-minute or 5-minute chart).
Step 2: Confirm Momentum with Indicators
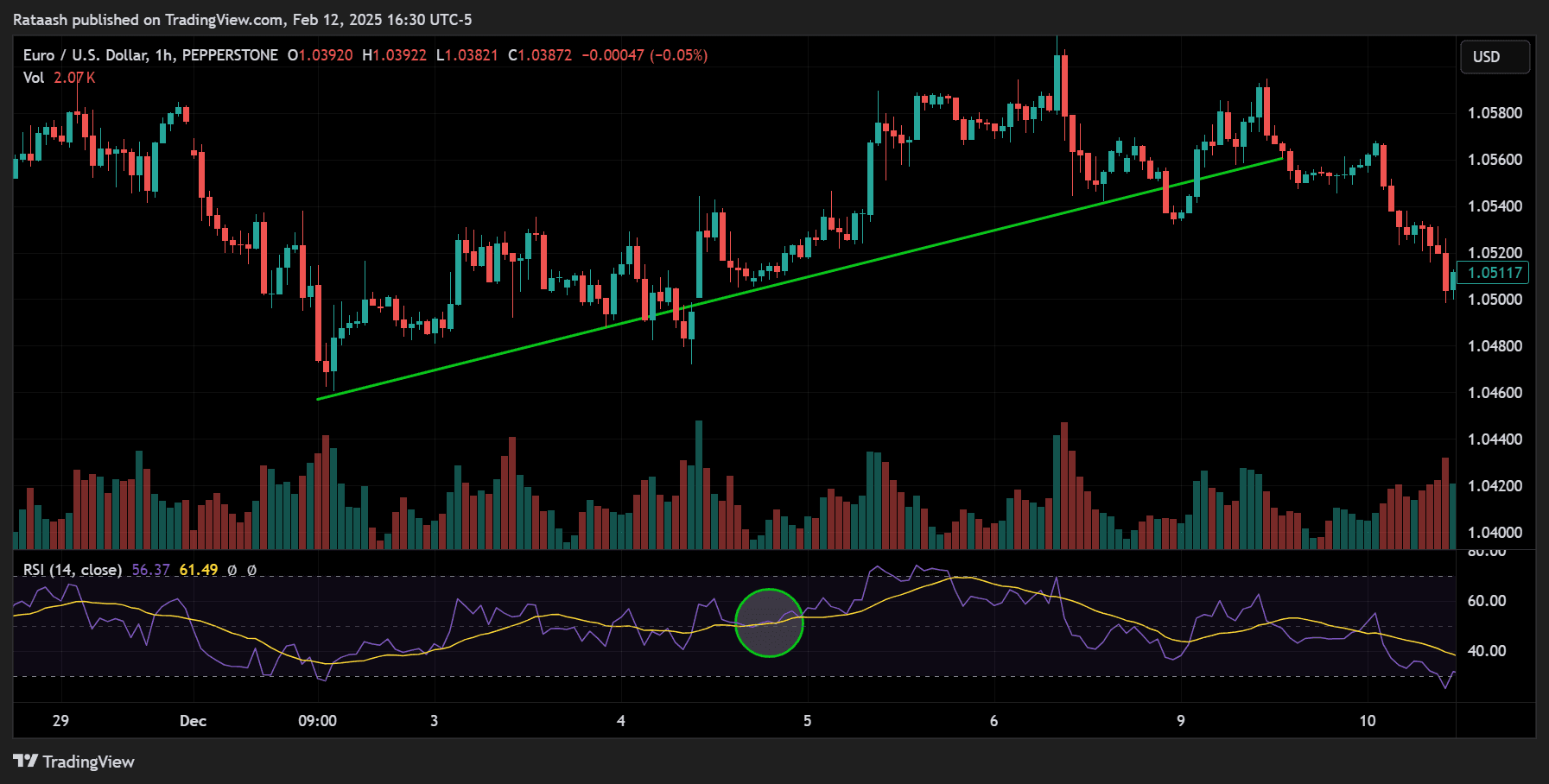
Once you identify the trend, confirm it with momentum indicators to ensure you’re not entering a market that is losing steam.
- Common Indicators: RSI, Stochastic, MACD histogram for momentum shifts.
- Confirmation: If the RSI is near the 50 level and pointing upward in a bullish trend, it might confirm ongoing momentum.
Step 3: Choose Optimal Entry Points
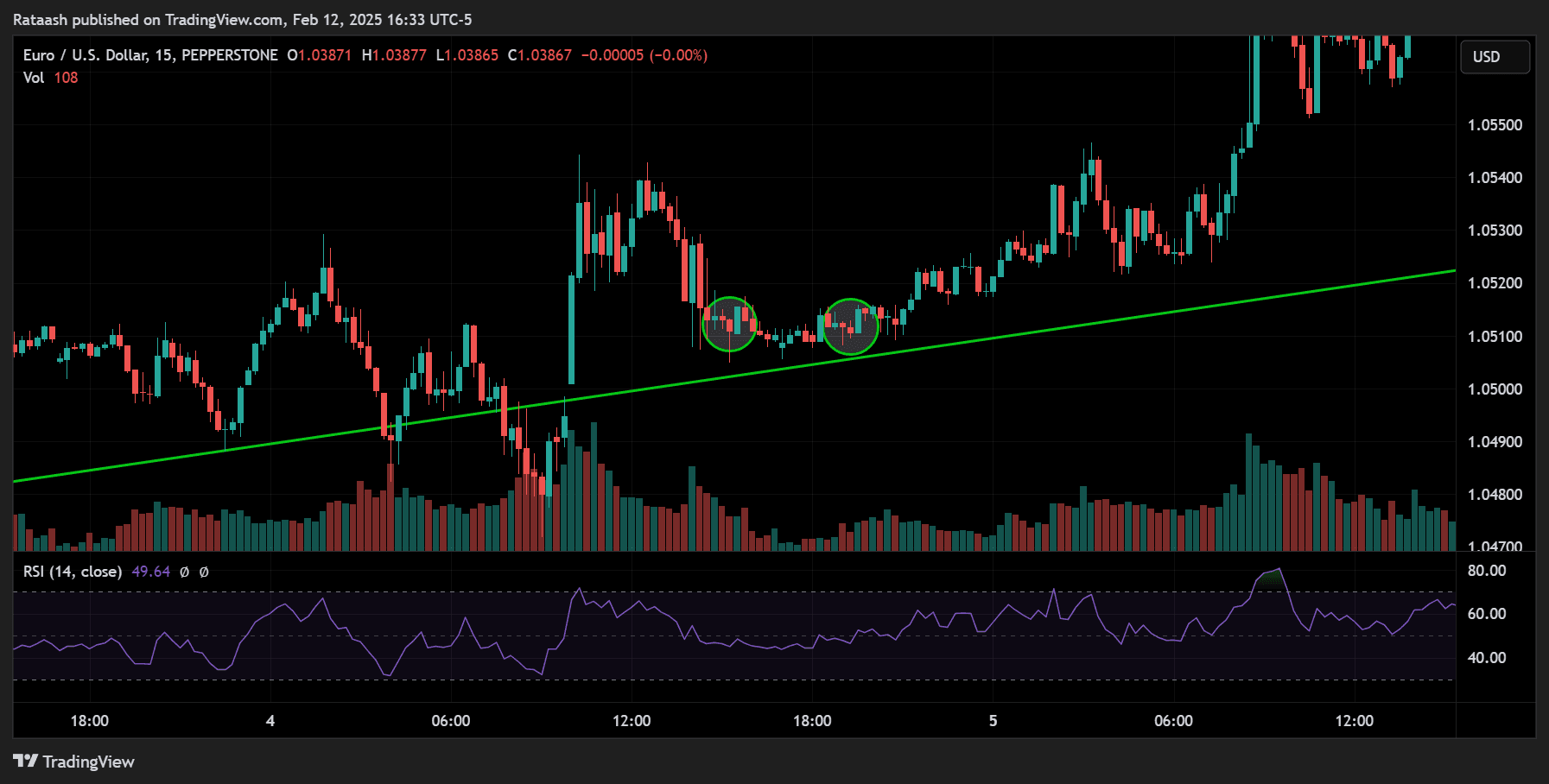
In a volatile market, prices can move fast, so timing is crucial. Look for clear chart patterns or indicator signals that line up with your identified trend.
- Examples of Entry Signals:
- Price touches a moving average (like the 20 EMA) and bounces toward the trend.
- Candlestick reversal patterns at key support/resistance.
- Momentum oscillators cross from oversold to upwards in a bullish trend (or overbought to downwards in a bearish trend).
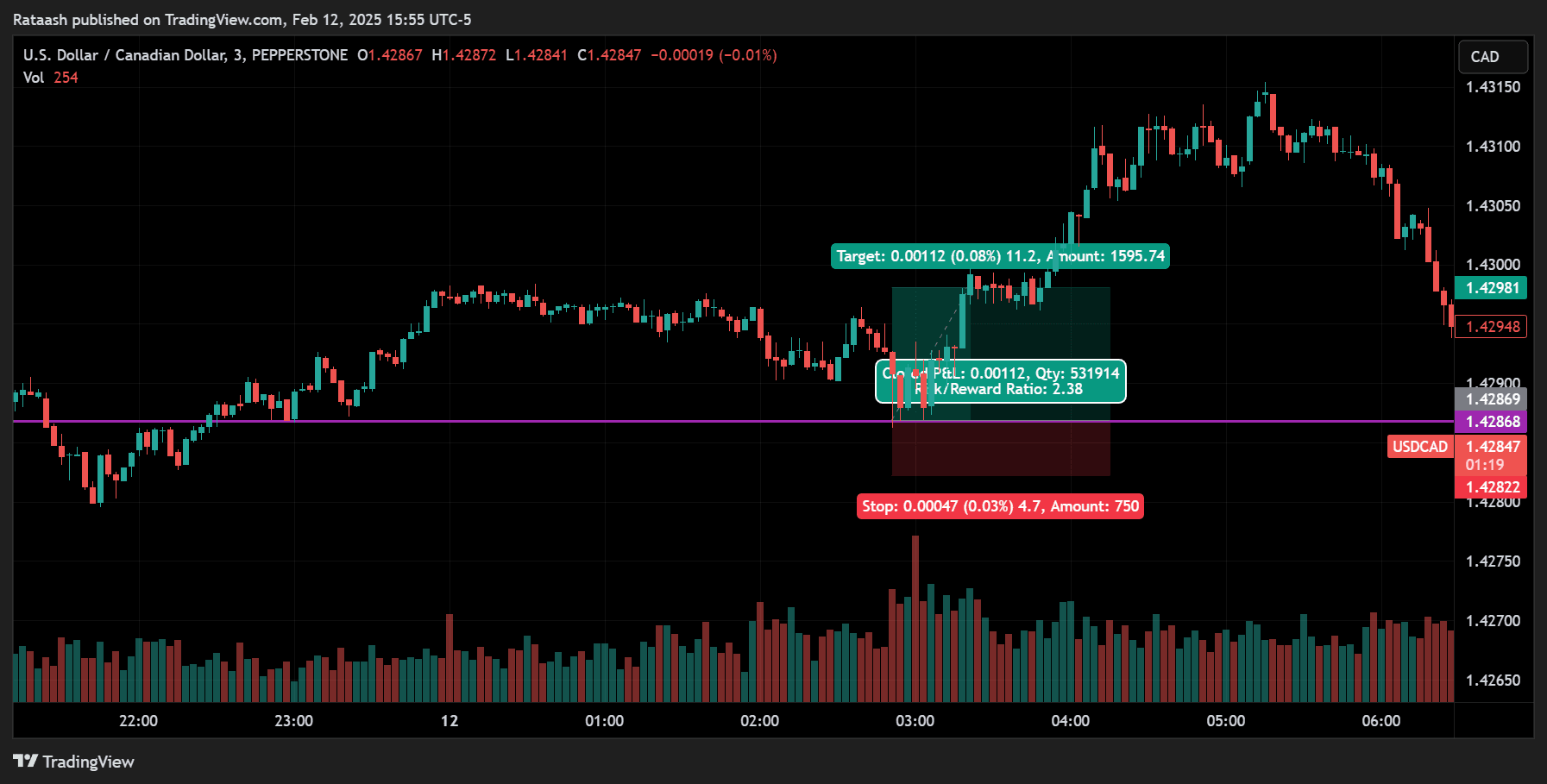
Step 4: Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
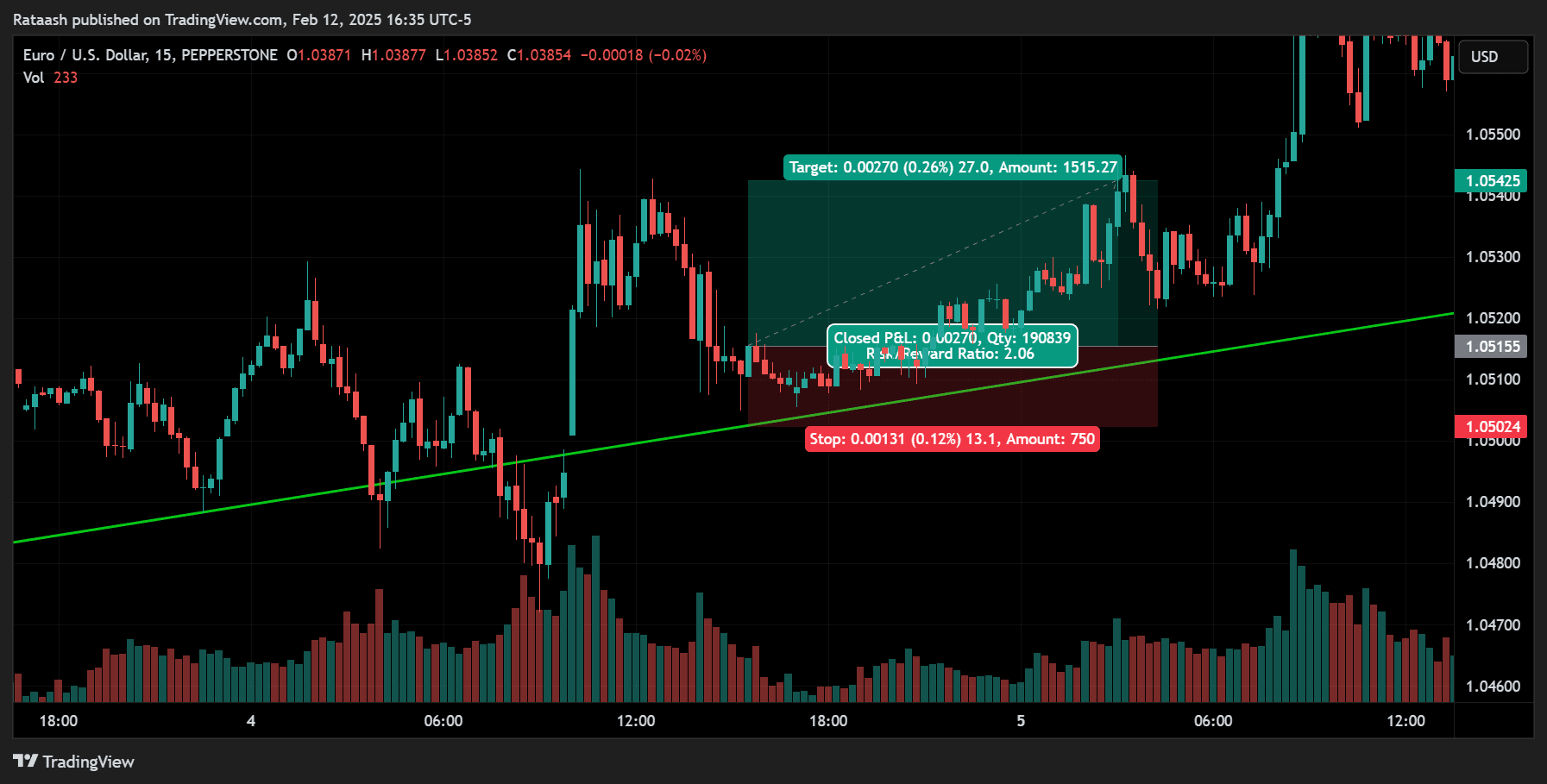
One of the cardinal rules of scalping is to always trade with a stop-loss. Since each trade aims for only a few pips, your stop-loss must be tight but also flexible enough to handle natural price fluctuations in a volatile environment.
- Stop-Loss Placement:
- Just below the most recent swing low for buy trades.
- Just above the most recent swing high for sell trades.
- Take-Profit Placement:
- Often set at 1:1 or 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio for scalping.
- You can also trail your stop as the price moves in your favor.
Step 5: Execute the Trade
Once you have all signals aligning trend direction, momentum confirmation, support/resistance levels, and risk parameters in place, it’s time to place the trade. Always double-check:
- Spread – In a very volatile market, the spread can widen unexpectedly.
- Position Size – Ensure you’re not over-leveraging.
- Risk-Reward – Confirm your stop-loss and take-profit levels align with your plan.
Step 6: Monitor Trades and Exit Quickly
Scalping requires real-time monitoring. In a fast-moving market, your profit target or stop-loss might be hit within seconds or minutes.
- Manual Exit – If price action stalls or reverses significantly, exit early instead of hoping it will turn back around.
- Trailing Stop – Some scalpers use a trailing stop to lock in gains if the trade moves favorably.
Step 7: Review and Refine
After each trade, document the setup, outcome, and any lessons learned. Over time, you will refine your strategy, identify recurring market patterns, and adjust to changing market conditions.
Risk Management and Position Sizing
Even though scalping is about small, quick profits, risk management is paramount. The key is ensuring a few losses don’t wipe out your entire account.
The 1% or 2% Rule
Many professional traders recommend risking only 1% or 2% of your trading capital per trade. For instance, if you have a $1,000 account and you risk 1% per trade, your maximum risk is $10 per trade.
- Why This Matters – Scalping can generate many trades per day. If you risk too much and lose multiple times in a row, it can significantly hurt your account.
Setting Tight Stop-Losses
A hallmark of scalping is the tight stop-loss. Given that you’re trading on 1-minute or 5-minute charts, you can typically place stops quite close to your entry.
- Example – You might place a stop-loss 5 pips away from your entry if you’re aiming for a 5–7 pip profit target.
- Volatility Consideration – Ensure your stop-loss is not so close that normal volatility triggers it prematurely.
Leverage Considerations
High leverage can amplify gains, but it can also magnify losses. While scalping can be profitable, using too much leverage is a common way beginners blow their accounts.
- Recommended Leverage for Beginners – 1:10 or 1:20 is often considered safer, though some brokers offer up to 1:500. Use leverage wisely.
Emotional Control and Trading Psychology
Trading psychology plays a massive role in scalping success. Quick decisions and rapid execution can lead to emotional pitfalls like fear and greed.
- Stay Disciplined – Follow your strategy’s rules. Don’t chase trades if you miss an entry.
- Avoid Revenge Trading – If you incur a loss, don’t try to immediately recoup it by placing impulsive trades.
- Take Breaks – Scalping is mentally taxing. Step away from the screen after a set number of trades or a specific time period.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Overtrading – Scalping can be addictive. Some traders jump on every small price move, ignoring proper setup confirmations.
- Solution: Stick to your trading plan. Define the number of quality setups you aim for each session.
- Ignoring Market Conditions – Not all times are good for scalping. Major news events can cause erratic moves that wipe out stops in seconds.
- Solution: Check the economic calendar. If you can’t handle the sudden volatility, avoid trading right before a critical announcement.
- Poor Stop-Loss Placement – Setting stops too tight or too far is equally problematic.
- Solution: Base your stop-loss on recent swing points or a logical distance given the currency pair’s average volatility.
- Using High Leverage Recklessly – New traders often get excited by the potential for big returns and max out their leverage.
- Solution: Use moderate or low leverage to give your scalping trades enough breathing room without risking a margin call.
- Lack of Consistency – Constantly switching indicators and strategies leads to confusion and inconsistent results.
- Solution: Pick a strategy and set of indicators, then stick to them for a defined trial period to gather sufficient data on performance.
Real-World Examples of Volatile Market Scalping
Example 1: GBP/USD During London Session
- Market Condition – The time is 09:00 GMT, and the London session is in full swing. GBP/USD has broken above its recent range.
- Trend Analysis – On the 15-minute chart, the 50 EMA is above the 100 EMA, confirming an uptrend.
- Indicator Confirmation – The 5-minute RSI is around 55, signaling mild bullish momentum.
- Entry Trigger – A pullback candle dips to the 20 EMA on the 1-minute chart but closes bullish.
- Trade Execution –
- Buy at 1.2405 with a Stop-Loss at 1.2400 (5 pips).
- Take-Profit at 1.2412 (7 pips).
- Outcome – Within 10 minutes, the price moves up to 1.2412, and the take-profit is hit.
Example 2: EUR/USD During New York Session
- Market Condition – Around 14:30 GMT, EUR/USD is experiencing sharp moves due to a US economic data release during the overlap of London and New York sessions.
- Trend Analysis – The 30-minute chart shows a clear downtrend, with the 50 SMA below the 100 SMA.
- Indicator Confirmation – The 5-minute Stochastic is in overbought territory (>80), indicating a potential short opportunity aligned with the downtrend.
- Entry Trigger – On the 1-minute chart, a bearish engulfing candle forms at a minor resistance level.
- Trade Execution –
- Sell at 1.0850 with a Stop-Loss at 1.0855 (5 pips).
- Take-Profit at 1.0842 (8 pips).
- Outcome – Price drops below 1.0842 within minutes, resulting in a successful scalp.
Practical Tips for Consistent Scalping Success
- Prepare a Trading Plan: Define your goals, risk parameters, and preferred indicators.
- Trade During High Volatility Periods – Focus on the London-New York overlap for the best price movements.
- Use a Demo Account First – Practice your scalping strategy in a risk-free environment before going live.
- Keep a Trading Journal – Record every trade, including your entry/exit points, stop-loss, take-profit, and the rationale. Analyze this data to identify patterns and improve.
- Manage Emotional States – If you feel stressed or fatigued, pause trading. Scalping with a clouded mind can lead to impulsive decisions.
- Monitor News Releases – High-impact news can drastically affect prices. Some scalpers thrive on this volatility, while others stay out to avoid unpredictable swings.
- Optimize Your Platform – Use a reliable broker with tight spreads and fast execution. If possible, ensure your trading platform is stable and set up with one-click trading for rapid execution.
- Stick to Simple Strategies – Overcomplicating your chart with too many indicators can create confusion, but it’s better to master a simple, robust setup.
Conclusion
The Volatile Market Scalping Strategy offers an exciting pathway for Forex beginners who seek quick profits. By capitalizing on the rapid price movements prevalent during high-volatility sessions, scalpers can open and close multiple trades in a short period, each targeting a small chunk of the market.
However, the fast pace of scalping is a double-edged sword:
- Risk Management becomes crucial to avoid letting one bad trade erase the gains from several winning trades.
- High Transaction Costs and widened spreads in times of extreme volatility must be accounted for to ensure that net profits remain healthy.
- Emotional Discipline is necessary to handle the mental pressure that comes from watching fast-moving prices and making split-second decisions.
For those willing to put in the time to study, practice, and discipline themselves, scalping in a volatile market can be rewarding. Start small, refine your techniques through a demo or micro account, and only scale up once you consistently see positive results. By mastering the fundamentals, understanding market volatility, employing the right indicators, and implementing strict risk management, you can position yourself for success in the fast-paced world of Forex scalping.
Ultimately, Volatile Market Scalping is all about harnessing the market’s momentum for short but frequent gains. With the right approach, tools, and mindset, it’s entirely possible to carve out steady returns even for a beginner venturing into the Forex world for the first time. Remember to remain patient, analytical, and committed to continuous improvement, and you will be well on your way to turning volatility into a powerful ally in your trading journey.